How to evaluate an image’s authenticity?
Synthetically modified videos, audios and images have the potential to manipulate public opinion on matters of public interest, and to fundamentally alter the fate of democratic processes.
Problem
In this fast paced world, one unchecked piece of information is often unwittingly followed by a waterfall of news coverage.
This puts outsized pressure on the fact checking departments of resource-constrained news organizations or expecting journalists to do their own fact checking.
This puts outsized pressure on the fact checking departments of resource-constrained news organizations or expecting journalists to do their own fact checking.
 Original image
Original image
Manipulated image
︎
Journalists and fact checkers rely on tedious processes like reverse image search or analytical tools with little context or explanation to validate the authenticity of images.


User Opportunity
Journalists
Who need to make sure an image is authentic before using it as a source or resharing it.
Fact checkers
Who need a reliable way to determine if an image is fake and understand the nature of its manipulation so that they can debunk it.
Academics
Who want to keep their technology up-to-date by training it on the latest datasets and socialize it with the right audience.
Who need to make sure an image is authentic before using it as a source or resharing it.
Fact checkers
Who need a reliable way to determine if an image is fake and understand the nature of its manipulation so that they can debunk it.
Academics
Who want to keep their technology up-to-date by training it on the latest datasets and socialize it with the right audience.

Assembler is a comprehensive
tool to analyze and detect digital & synthetic manipulation in images.
Assembler makes predictions based on the signals produced by the contributing detectors on the image uploaded, and their degree of similarity to those obtained from our training data, which is made up of nearly 50,000 known manipulated and non manipulated images.
tool to analyze and detect digital & synthetic manipulation in images.
Assembler makes predictions based on the signals produced by the contributing detectors on the image uploaded, and their degree of similarity to those obtained from our training data, which is made up of nearly 50,000 known manipulated and non manipulated images.
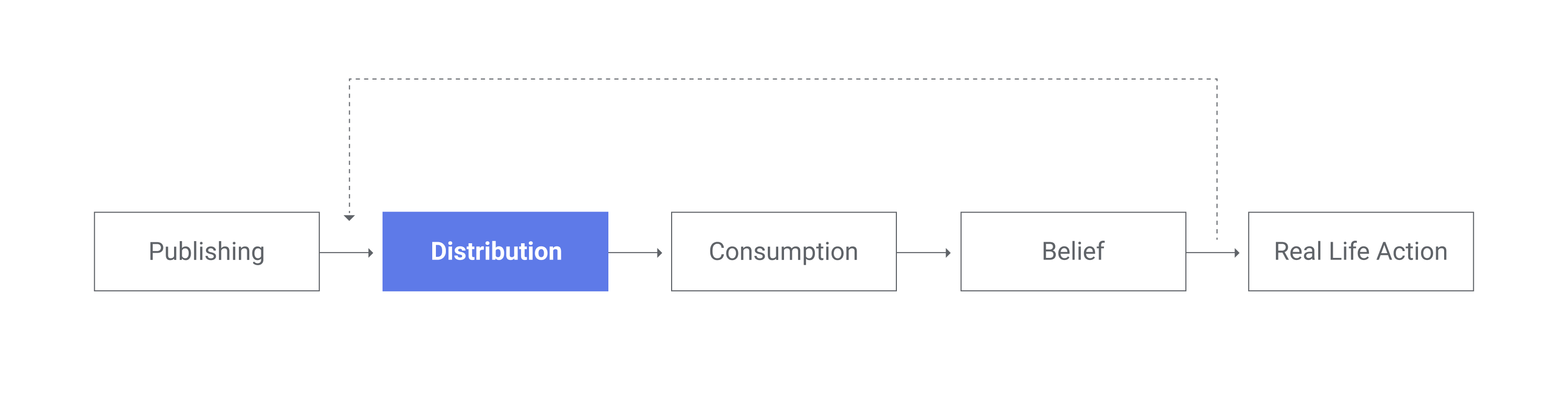
Assembler addresses disinformation at the distribution stage by giving parties that play a strong role in dissemination (fact-checking news organizations, large news organizations and online platforms) a tool to detect manipulation in media.